Moving Beyond Traditional Security: Why the SASE Framework Matters
Organizations across regulated industries like healthcare, finance, legal, and pharmaceuticals face relentless security challenges. The increasing use of cloud applications, remote workforces, and sensitive data flows has undercut the effectiveness of legacy network perimeters. Enter the SASE framework, a comprehensive approach designed for the new world of flexible business operations and cloud-first strategies. But what exactly is the SASE framework, and why is it critical for small to mid-sized businesses (SMBs) in sectors that must maintain strict compliance and data protection?
The term SASE, which stands for Secure Access Service Edge, represents a modern security and networking model that brings security and connectivity together in one cohesive platform. By understanding the SASE framework, business leaders and IT teams can see how it goes far beyond patchwork security solutions or outdated hardware. It’s not an incremental upgrade, SASE architecture is a shift, bringing together network security, cloud integration, and compliance in a way that feels seamless for both users and administrators.
For businesses that handle protected health information (PHI), client financial data, legal files, or proprietary research, SASE network security offers a pathway to compliance and efficiency. The model is drawing considerable attention from security officers, IT managers, and compliance experts looking for smart ways to handle modern risk. SASE meaning isn’t just a buzzword; it describes an architecture that delivers cloud-native security as a service at the edge of your network, wherever your users and devices are located.
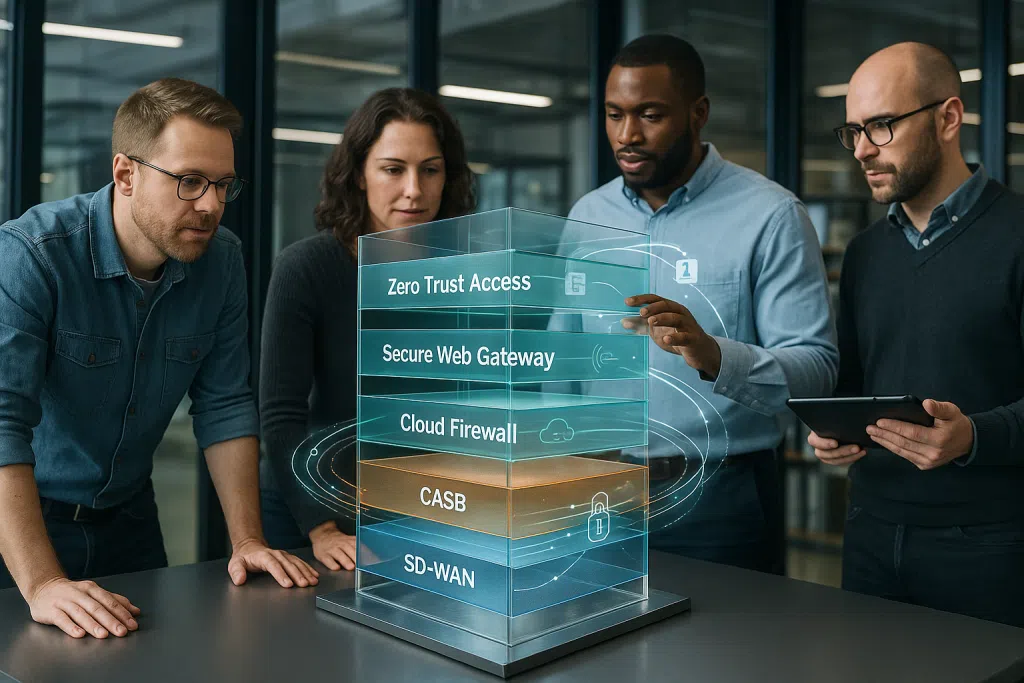
Instead of relying on multiple standalone technologies, SASE security combines core capabilities like zero trust network access, secure web gateways, firewall-as-a-service, cloud access security brokers, and more, all delivered from the cloud. Whether you’re managing remote workers, distributed offices, or cloud-based apps, SASE lets SMBs apply the same security policies and controls everywhere, reducing the chance of gaps or oversights.
Security and IT teams shouldn’t have to juggle endless appliances or complex configurations. The SASE framework reduces complexity. It steers companies toward streamlined IT operations and a strong security baseline that doesn’t get in the way of business growth.
Ready to see how your organization could benefit from the SASE approach? Book an initial Discovery meeting with our team to learn how Blueclone Networks can help you assess, adopt, and optimize SASE security: Schedule a Discovery Meeting.
Key Components of SASE Architecture: Security and Networking Converge
Diving deeply into the SASE architecture, it’s essential to understand the individual elements that anchor this framework. Unlike older network security models that separate security and networking, and often require complex integrations, SASE merges these functions at the network’s edge and delivers them as cloud-managed services. This design is especially valuable for organizations in regulated industries faced with strict cybersecurity and compliance requirements.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
ZTNA ensures that nobody, whether internal staff or external users, gets access to resources without proper authentication. Credentials, device posture, user roles, and context are constantly evaluated before granting network access. This reduces the risk of lateral attacks and minimizes impact if credentials are compromised.
Secure Web Gateway (SWG)
An SWG filters unsafe internet traffic and blocks access to suspicious or non-compliant sites. It enforces web policy controls, scans outgoing and incoming traffic for malware, and can prevent users from transferring sensitive business data to unauthorized destinations.
Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
CASBs act as gatekeepers for cloud services, offering visibility and control over how employees interact with SaaS applications like Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace. CASBs help enforce policy, monitor user activity, and detect slow compliance drift before it becomes a risk.
Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS)
Delivered from the cloud, FWaaS offers firewall functions like intrusion prevention, traffic filtering, and VPN support across multiple sites and remote devices. This means IT teams no longer have to maintain a collection of physical and virtual firewalls at every branch location; SASE handles it through a unified cloud portal.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP within SASE security settings automatically detects and blocks unauthorized sharing or transfer of regulated data, such as HIPAA-protected health records or PCI-covered payment details.
Centralized Policy Management
One of the most valuable aspects of the SASE framework is unified policy enforcement. Administrators define security settings, access rights, and compliance rules once, and these policies automatically apply to every user, device, and office, no matter where they are.
With these interconnected components, SASE meaning transforms from a high-level concept into a daily practice. In legacy networks, securing a distributed workforce or multi-cloud setups would require dozens of manual configurations and appliances. With SASE architecture, the burden is reduced. Everything is managed in a single dashboard and pushed to the edge in real-time.
SMBs in legal, finance, or healthcare fields benefit especially. A law firm with staff frequently traveling for depositions, a physician group with satellite clinics, or a financial advisory practice operating in a hybrid environment, these businesses need singular, consistent controls. SASE network security delivers this without the pain and time investment associated with perpetual hardware upgrades or manual patching.
At the heart of this approach is the cloud. Security updates, threat definitions, and compliance rules are maintained by your provider, ensuring you remain protected and up to date without constant manual intervention.
SASE Network Security vs. Traditional Security: What’s the Difference?
For many small and mid-sized organizations, the leap from legacy perimeter security to SASE network security can feel daunting. There’s a comfort in the familiar: firewalls, VPN concentrators, intrusion prevention systems situated at a well-defined network edge. Yet, business reality has shifted. In 2026, the “edge” is wherever your data, users, and devices happen to be: the office, a remote home, or a cloud app on a smartphone.
Traditional Network Security:
Historically, security took a castle-and-moat approach. IT teams deployed hardware at central gateways, such as routers, firewalls, and dedicated proxy servers, to segment and protect internal systems. This model functioned when most resources were on-premises, users worked in offices, and the internet was largely kept at bay.
Emergence of SASE Security:
The expansion of cloud computing, mobile devices, and work-from-anywhere policies changed this dynamic. Instead of funneling everyone through a single point, people now work in different locations, on various devices, using SaaS apps that don’t always connect back to corporate networks first. This exposes businesses to risks if conventional controls leave “blind spots”, gaps where data is not fully protected or monitored. SASE security responds to this by delivering persistent enforcement of security policies at each connection point, no matter where it originates.
Key differences can be broken down as:
- Flexibility: Traditional models struggle to keep up with a mobile workforce and multi-cloud environments. SASE means policies follow your users everywhere without the need for constant reconfiguration.
- Scalability: As business expands to new locations or adds remote users, adding capacity under traditional models means new hardware and complex site-to-site tunneling. SASE makes scaling as simple as provisioning new licenses or adjusting settings in the cloud.
- Visibility: SASE provides detailed insights into traffic and threats across all locations, including encrypted cloud traffic, reducing the “dark corners” that attackers often exploit.
- Compliance: Applying HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or GDPR controls consistently can be tough with scattered systems. With SASE architecture, compliance enforcement is automatic and auditable, making regulatory audits less burdensome.
According to a 2025 Gartner report, 60% of enterprises will have a clear SASE adoption strategy in place by late 2026, compared to less than 10% in 2018. Integrating SASE security is becoming standard practice, not just a novel solution for tech-forward giants.
If you’re evaluating whether to transition from old network models or are unsure how to unify cloud, remote, and office security, a structured SASE assessment can clarify the steps and priorities for your organization. Book an initial Discovery meeting now and let Blueclone Networks walk you through your options and a realistic adoption timeline.
How SMBs in Healthcare, Finance, and Legal Benefit from SASE Meaning
For regulated SMBs, adopting the SASE framework is not simply about keeping up with technology trends, it’s about survival and growth under strict compliance obligations. Each industry faces unique threats and requirements, but SASE architecture levels the playing field by offering a scalable, adaptable, and compliant foundation.
Healthcare
Healthcare organizations must ensure patient records are protected at all times and maintain strict HIPAA compliance. SASE security helps enforce access controls, data loss prevention, and audit trails, whether clinicians are accessing cloud-based electronic health records from the hospital, a clinic, or a mobile device at home. Secure access service edge models minimize unauthorized entry by applying continuous authentication and device validation. This also supports complying with Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH) requirements.
A leading example: A growing physician network in New Jersey implemented SASE to secure remote diagnostics, telemedicine, and collaboration across their clinics. They reported a 29% reduction in compliance-related incident tickets within six months, according to a survey they provided to Blueclone Networks.
Legal Services
Law firms are entrusted with sensitive case files, contracts, and communications. SASE architecture means legal teams and associated contractors can access encrypted files and cloud-based case management tools with granular, role-based controls, no more risk from vulnerable email attachments or unsanctioned file-sharing platforms. Whether working from court, home, or satellite offices, every session and file transfer is protected under firm-wide SASE network security policies.
Finance
Financial offices face phishing, ransomware, and regulatory audits with increasing regularity. With SASE, policies like MFA (multi-factor authentication), transaction logging, and cloud access monitoring are all centrally managed. When paired with secure access service edge methods, even pop-up branches or remote financial planners can work with sensitive client data in full compliance with FINRA and PCI-DSS requirements.
A recent IDC survey (2026) highlighted that SMBs using SASE architectures experienced up to 45% quicker compliance audit cycles and halved their incident response effort, freeing their internal teams for strategic initiatives.
Professional Services and AI Integration
CPAs, consultants, and engineering firms increasingly need to share data with clients, regulatory agencies, and AI-powered applications. SASE controls manage how third-party and AI-driven tools access sensitive financial or client records, placing tight controls on API interactions and data flows.
In all these sectors, SASE meaning comes alive as “security everywhere, enforced the same way”, not just a theoretical construct, but a real-time, auditable, and scalable protection layer.
Implementing a SASE Strategy: Steps for SMBs Ready to Modernize Network Security
While the benefits of SASE are clear, effective adoption requires a defined strategy tailored to your organization’s unique needs and regulatory context. SASE implementation is not a one-size-fits-all process, a thoughtful approach ensures both compliance and operational efficiency.
Assess Your Security Baseline
Chart out your current IT infrastructure, including locations, user profiles, cloud services, and compliance requirements. Identify where legacy controls are insufficient, areas frequently targeted by phishing, gaps in remote access security, or unmanaged cloud application use.
Define Compliance and Access Policies
Work with compliance teams and service providers to establish the right policies based on HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR, or other relevant frameworks. Document acceptable use, data sharing requirements, authentication standards, and incident response workflows.
Choose the Right SASE Provider and Tools
Seek partners with experience in regulated sectors. Consider S.A.S.E. security vendors who support integrations with your existing cloud apps and provide proven support for data privacy, centralized management, and secure migration of sensitive workloads.
Pilot and Integrate SASE Services
Roll out SASE functionality in phases. Begin with cloud application protection and secure remote access features. Expand to include unified policy management, secure web gateways, and automation for network segmentation.
Train and Support your Workforce
Provide user education on new authentication steps, access procedures, and why security hygiene is essential. SASE’s meaning should be clear to all employees, not just IT staff.
Monitor and Continuously Improve
Leverage the real-time visibility and analytics provided by SASE architecture. Continuously monitor access patterns, incident logs, and compliance metrics. Use these insights to optimize security posture and update policies as threats evolve.
According to Forrester’s 2026 Security Transformation Guide, organizations that followed a staged, collaborative approach to SASE adoption saw better user acceptance and stronger regulatory outcomes than those treating it as a simple technology refresh.
If you want to understand how your business can transition smoothly, staying agile while meeting compliance mandates, schedule a Discovery meeting with Blueclone Networks. We’ll map out the transition, explain the tradeoffs, and forecast how SASE adoption impacts costs, compliance, and productivity.
Future Trends: SASE Security and the Evolution of Network Protection
The adoption of the SASE framework is not just a trend but a critical shift toward comprehensive, cloud-native security and network management. With cyber threats growing and workplace flexibility becoming the norm, SASE architecture offers a future-proof way to keep organizational data protected and managed.
Some emerging trends to watch include:
Integration with AI-Powered Defense Tools
SASE solutions are adding machine learning engines that spot anomalous traffic or suspicious behavior in real time. This helps regulated SMBs stay one step ahead of cybercriminals who use advanced, fast-moving attack techniques.
Support for IoT and Edge Devices
More medical devices, point-of-sale terminals, and industrial controls now connect directly to cloud systems. SASE security frameworks can inspect and manage data moving between these smart endpoints, extending compliance policies to every corner of an organization’s infrastructure.
Unified Threat Intelligence Sharing
Modern SASE platforms tap into global feeds of cybersecurity data, sometimes updated hourly, to identify fast-spreading malware or vulnerabilities. Threat intelligence gathered by leading SASE providers is shared instantly across all client environments, shielding even small businesses from widespread attacks.
SASE and Regulatory Standards Alignment
Industry bodies and compliance authorities are starting to recognize SASE controls as effective measures for safeguarding sensitive data. Recent updates in HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and regional frameworks reference SASE elements as best practice for secure access and robust audit trails, as detailed in Gartner’s 2026 Market Guide for SASE.
In summary, the future of SASE network security is about proactive defense, automation, and seamless cloud integration, all under an auditable, compliant, and scalable framework.
Take the first step towards smarter security and compliance for your SMB: Book an initial Discovery meeting with Blueclone Networks and let us help you design a modern, resilient, and effective SASE strategy.
FAQs About the SASE Framework
SASE stands for Secure Access Service Edge. Its main purpose is to combine network security and connectivity services into a cloud-based framework that delivers consistent protection and policy enforcement anywhere users or data are located. It’s designed to secure organizations as they transition away from traditional office-bound networks to cloud-first, distributed operations.
SASE enhances data protection by centralizing policy enforcement, identity management, and encrypted access controls. This is critical for businesses in healthcare, finance, or legal sectors, where data leakage or improper sharing can result in violations and fines. The SASE framework ensures only authenticated, authorized users can access sensitive information, no matter where they work.
Yes, SASE architecture typically replaces much of the on-premises security hardware like firewalls, VPN concentrators, and proxy appliances. It does so with cloud-managed services that deliver the same or stronger controls, providing scalability, easier management, and quicker policy updates. However, migration should be planned carefully to ensure no gaps.
Implementation time varies. SMBs with basic cloud and remote access needs can often launch core SASE components within a few weeks, especially with experienced providers. More complex environments, legacy integrations, or advanced compliance requirements may take several months for phased rollout and full policy adoption.
Focus on vendors with a history of serving regulated industries, strong experience in compliance support, and proven integrations with your existing cloud apps and endpoints. Also, evaluate dashboard usability, the scope of analytics and reporting features, and the availability of 24/7 support. Most importantly, the provider should demonstrate how their SASE framework will map to your compliance and security priorities.