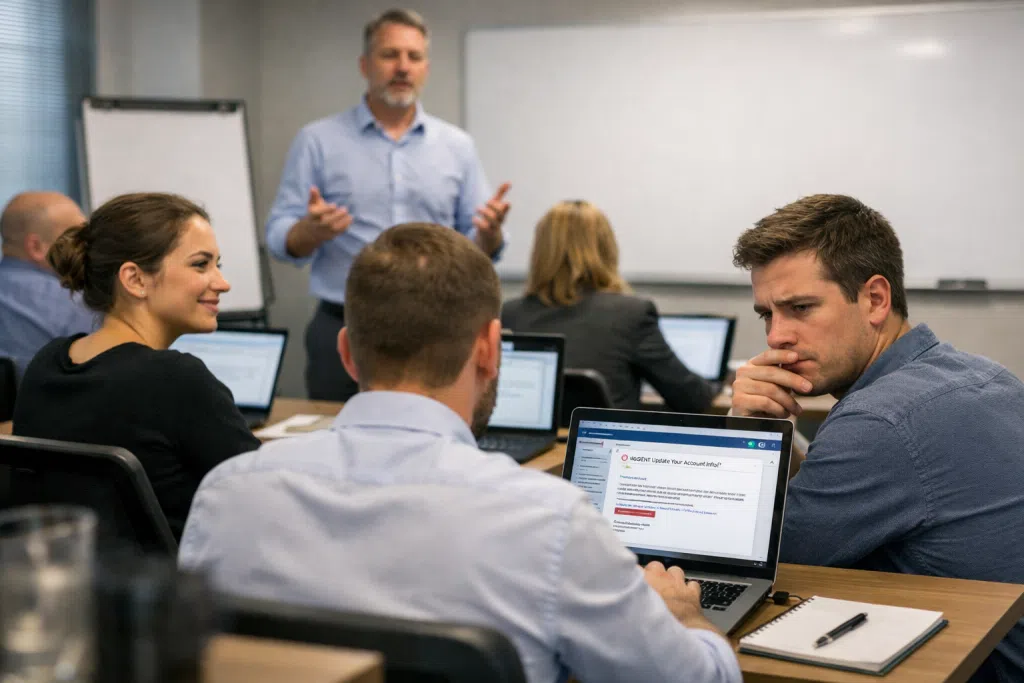
Email is the lifeline of communication for healthcare, finance, law, and many other highly regulated industries. For small and medium-sized businesses in Central New Jersey and surrounding regions, robust email security training is not a “nice to have”, it’s a necessity. Yet even diligent organizations with regular training sessions may overlook subtle but vital components that leave them exposed to sophisticated cyber threats. This article dives into the overlooked aspects of email security training, providing practical guidance for businesses that are serious about reducing risk.
Beyond the Basics: What Typical Email Security Training Leaves Out
Despite the frequency of awareness campaigns, most email security training programs lean on common themes: recognizing basic phishing scams, not clicking suspicious links, and maintaining strong passwords. While important, these basics don’t address the tactics used by today’s attackers.
Attackers have grown more adept, deploying social engineering, business email compromise (BEC), and malware-laden documents masked as routine correspondence. Relying on dated content or generic modules can give employees a false sense of confidence. For healthcare, legal, and finance sectors in New Jersey, this can lead to HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or FINRA violations with severe compliance penalties.
Common Gaps in Traditional Training:
- Lack of Advanced Phishing Detection: Attackers use convincing language and even mimic a company’s communication style. Template-based training rarely drills down into real examples that workers in regulated industries might actually encounter.
- Inattention to BEC and Impersonation: While standard programs discuss generic phishing, many don’t address business email compromise, where attackers pose as executives or vendors to reroute payments or extract sensitive data.
- Outdated Threat Models: Cyber tactics evolve rapidly. Training modules that aren’t updated regularly fail to cover emerging scams and new malware payloads, leaving staff ill-prepared.
- No Contextualization for Compliance: Specific guidelines for HIPAA IT compliance, legal privilege, or confidential financial exchanges are rarely integrated into general security awareness programs.
A truly effective email security training program incorporates evolving threat patterns, contextualizes learning to each sector, and uses real-world data from the latest attacks. Periodic refreshers anchored in recent incidents tailor defenses to actual risk.
Connect with Blueclone Networks now to discuss custom security awareness programs designed to address these sophisticated threats and compliance demands: Book a meeting.
Integrating Phishing Detection and Response Into Everyday Practice
Phishing is responsible for a huge percentage of breaches each year, and New Jersey organizations remain high-value targets due to dense regulatory oversight. Yet, threat simulation is often limited to email blasts with obvious clues, hardly sufficient for a motivated attacker. Studies, including a 2026 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, highlight that 74% of breaches involve the human element, stressing the need for hands-on, frequent testing rather than passive modules.
Making Phishing Training Realistic:
- Regular, Sector-Specific Simulations: Employees in healthcare, financial, or legal roles encounter unique threats. Effective training uses legitimate-looking simulations, such as vendor impersonation or urgent legal notifications, mirroring what staff might see in the wild.
- Encouraging Prompt Reporting: Staff should feel confident reporting not just suspected phishing emails, but also misdirected or unusual requests, without fear of negative repercussions. Make this a routine, not an afterthought.
- Drills Beyond Email: Since phishing also occurs through SMS, messaging platforms, and even phone calls, training should cover these alternative vectors for a holistic defensive posture.
While phishing detection remains a priority, many organizations lack a defined process for what happens after a phish is identified. Rapid escalation paths, forensic review, and communication protocols should be baked into your training curriculum. This moves the response from being reactionary to proactive and coordinated.
According to the SANS Institute (2026), companies that blend simulated phishing with practical, scenario-based exercises experience a 50% lower rate of successful attacks compared to those relying on basic online modules.
For modern SMBs, the gold standard for email security training is a living, breathing program, constantly evolving, aligned to current threat intelligence, and focused as much on positive reinforcement as on technical skill-building.
Addressing Business Email Compromise: The Silent Threat
Business email compromise is perhaps the most financially damaging cybercrime targeting regulated industries in New Jersey. These attacks bypass traditional spam and malware filters by manipulating human trust. An attacker posing as a managing partner, CFO, or vendor requests a payment, wire transfer, or the release of confidential information. It only takes one employee to miss subtle clues for a breach to occur.
Why Current Training Misses the Mark:
- Focus on Obvious Red Flags: While employees learn to spot misspellings and sketchy links, modern BEC attacks use correct spelling, titles, and context gleaned from social media or previous breaches.
- Lack of Workflow Guidance: Real BEC events often happen during periods of high activity, quarterly closes, legal filings, or after office relocations. Training seldom incorporates stress or workload-based exercises.
- Overlooking Verification Protocols: It’s not enough to say, “verify requests.” Employees must be taught specific call-back procedures, escalation paths, and documentation protocols to detect and stop impersonation.
The FBI’s latest Internet Crime Report cites BEC as responsible for more financial losses than phishing or ransomware combined, with average payouts topping $125,000 per incident in 2023.
Building a BEC-Resilient Workplace:
- Role-Specific Training: Tailor modules for finance, legal, and healthcare professionals, introducing scenarios tied to their daily workflows, including realistic fraudulent invoice and contract requests.
- Culture of Verification: Create an environment where double-checking unusual requests, even from the CEO, is understood as policy rather than caution. Simulate periods of high stress or unusual activity in drills to see how employees respond under pressure.
- Explicit Communication Channels: Document and regularly update procedures for high-value transactions. Use tamper-proof channels (such as encrypted phone calls or secure messaging tools) for confirming changes related to finances or sensitive information.
Staff primed with practical knowledge and clear, easy-to-follow playbooks are your best defense. This is especially relevant for co-managed IT teams, where internal approvals and external vendor communications often intersect.
Connect with Blueclone Networks now for advanced email cyber security strategies focused on BEC risk management and real-world defense: Book your strategy session.
Leveraging Secure Email Hosting and Advanced Technical Controls
Even the most robust training can fail if your technical infrastructure is outdated or misconfigured. Secure email hosting acts as a first line of defense, combining encrypted communications, real-time threat detection, and policy-based controls. In an era where cloud collaboration and remote work are standard, relying solely on on-premises or legacy email solutions is risky, especially for SMBs in regulated industries.
Critical Features to Prioritize:
- End-to-End Encryption: Sensitive client data, such as patient records, legal documents, or financial statements, should never travel unencrypted. Ensure hosting services comply with standards like HIPAA or FINRA.
- AI-Driven Threat Detection: Newer secure email hosting platforms deploy artificial intelligence to spot zero-day phishing tactics, preventing malicious content from reaching the inbox.
- Automated Quarantine and Alerts: Real-time blocking and alerting for unusual login attempts, malware attachments, or suspicious file types add a dynamic layer to email cybersecurity.
- Multi-Factor Authentication and User Access Controls: Requiring multiple factors for logins, especially on mobile devices or for staff with privileged access, neutralizes many common attacks.
- Advanced Filtering and Reputation Blacklisting: Scanning inbound and outbound traffic for signs of data exfiltration or spoofed sender domains should be mandatory.
These controls protect not only the organization but also clients and patients, reducing liability. According to Gartner’s Email Security Market Guide (2026), organizations using AI-enabled secure email hosting platforms saw a 60% reduction in successful phishing-related incidents compared to those relying solely on awareness training.
Integrate Technical Solutions with Human Vigilance
Secure email hosting solutions, like those managed by Blueclone Networks, bridge people and technology. For law firms, medical practices, and financial offices in Central NJ, expert configuration ensures compliance and helps internal IT focus on priorities beyond day-to-day threat hunting.
Couple advanced technical controls with ongoing training for a double-layered approach, one that defends against both automation and social engineering.
Cultivating a Security Awareness Culture That Sticks
Effective email security training is much more than quarterly webinars or check-the-box compliance eLearning. What truly matters is whether your organization has shaped a lasting culture of security awareness, one where staff continuously look for threats, discuss risks, and share new findings.
Elements of a Strong Security Awareness Culture:
- Leadership Buy-In: Executive teams must visibly champion security efforts. Their participation, whether in workshops or communications, signals importance throughout the company.
- Micro-Learning and Real-Time Updates: Short, targeted lessons distributed regularly, via chat channels, emails, or quick video clips, keep users informed on the latest phishing campaigns, emerging attack vectors, and industry-specific news.
- Positive Reinforcement: Recognize employees who successfully spot threats or follow secure procedures. Rewarding vigilance encourages participation and removes the stigma of error reporting.
- Peer Learning Workshops: Bring teams together to analyze anonymized incidents, including near-misses or real attacks (with sensitive details masked). This builds practical knowledge and demystifies the reporting process.
- Transparent Metrics: Display organization-wide results without shaming. Show improvements in phishing detection rates, reduced click-throughs, or the number of security questions asked during verification. Seeing progress motivates improvement.
Regulated industries in New Jersey demand more than just compliance; they require an environment where every employee feels responsible for data protection. Invest in ongoing, accessible education shaped by real industry risks and adjusted as cybercriminal tactics evolve.
Building this culture isn’t fast, but organizations that do consistently face fewer breaches and recover faster when attacks do occur.
Practical Steps for Implementing an Effective Email Security Training Program
If you’re looking to revamp or launch a new email security training initiative, it helps to break the process into actionable phases. The following steps ensure your strategy covers both foundational essentials and advanced protective measures, without overwhelming your team.
- Conduct a Risk Assessment: Begin with a formal review of your current email security posture. List known gaps, compliance obligations, department-specific risks, and any recent incidents. For regulated industries, this includes reviewing obligations under HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or attorney-client privilege.
- Segment Your Audience: Not all employees face the same risks. Create role-based tracks so your legal professionals, finance managers, and healthcare staff receive the most relevant scenarios and response playbooks. Customizing training modules ensures greater engagement and retention.
- Layer Learning Modalities: Mix live workshops, micro-learning delivered via email, and hands-on phishing simulations. Interactive sessions, including real incident reviews, are proven to boost knowledge retention compared to passive video modules. Encourage open Q&A and “what-if” discussions.
- Establish Feedback Loops: Build mechanisms for employees to suggest improvements or flag confusing scenarios. An anonymous feedback option helps identify knowledge blind spots. This bottom-up feedback becomes critical input for future iterations of your program.
- Measure and Benchmark Progress: Track your organization’s click rates on simulated phishing, average incident reporting time, and percentage of users following verification protocols. Share these metrics with your leadership team so cybersecurity becomes a shared accountability, not just an IT concern.
- Integrate Technical Policies: Training is far more effective when paired with enforced policies. Roll out email banner warnings for external messages, mandatory reconfirmation for wire transfers, and automated lockout protocols for suspicious logins. These controls reinforce user guidance with technology.
- Schedule Regular Refreshers: Cyber threats and attack methods are always shifting. Schedule small but frequent updates, even a monthly newsletter with real case studies or new attack types, can keep security awareness top of mind.
- Include Third-Party Communication Risks: Remind staff to verify the legitimacy of messages from partners, vendors, or regulators. Supply chain attacks are rising, and trusted brand logos or known names do not guarantee safety.
By approaching security training as a living system, one that adapts and grows, you build a team that not only avoids “gotcha” moments but actively strengthens your organization’s cyber resilience.
The Importance of Testing, Analytics, and Continuous Evaluation
A strong email security posture is maintained not just through education, but by constant testing and analytics. Organizations that see the greatest reduction in risk are those committed to learning from mistakes, tracking improvement, and responding quickly to change.
- Simulated Attacks at Random Intervals: Rather than set annual testing periods where staff may be on alert, organizations should run unexpected phishing scenarios. This gives a realistic measure of daily vigilance and readiness, providing valuable insights for further training.
Continuous Improvement: The Role of Co-Managed IT and External Experts
While your internal IT or compliance teams are the first line in building and maintaining email security, external experts bring a crucial perspective and resources. The pace of new threats, changes in regulatory guidance, and the complexity of secure cloud email systems mean that partnerships and regular assessments are invaluable.
Key Benefits of External Collaboration:
- Unbiased Security Audits: Independent assessments reveal blind spots overlooked by internal teams too close to daily routines. For healthcare, finance, and legal sectors in New Jersey, this is vital for maintaining confidence during external audits.
- Up-to-Date Threat Intelligence: Security vendors and co-managed IT services monitor attacks across multiple clients and industries, identifying new phishing campaigns or BEC tactics faster than individual firms can.
- Customized Security Awareness Programs: Vendors like Blueclone Networks develop training that reflects your industry, unique workflows, and compliance requirements, far beyond off-the-shelf eLearning.
- Incident Response Playbooks: Predefined escalation, investigation, and communication plans ensure your team knows exactly what to do when a threat is spotted, reducing response time and limiting breach impact.
According to a 2026 study by CSO Online, organizations leveraging co-managed IT services detected and neutralized email threats 40% faster than those managing everything in-house.
Strong partnerships augment your resources, provide a reality check on internal gaps, and help keep training as adaptive as the threats you face.
Ready to close the gaps in your email security training? Connect with Blueclone Networks now to create a security-first culture and technical foundation: Book your consultation today.
Emerging Trends in Email Security for SMBs
With the increase in remote work, cloud collaboration, and AI-driven cyberattacks, small and mid-sized businesses in regulated industries must adapt their email security training faster than ever before. Here are key trends every compliance-conscious organization should keep on their radar:
- Deepfake and Voice Phishing: Attackers now use AI-generated audio or video to impersonate executives or regulators, making verification protocols even more vital. Security awareness now needs to include recognition of video and voice manipulation tactics, especially during sensitive business processes.
- Contextual Awareness Training: Rather than static courses, top programs now leverage data from real, recent incidents, either within the company or aggregated from industrywide events. This adaptive approach ensures ongoing relevance and higher engagement.
- Integration with Collaboration Tools: Email is not the only channel at risk. Training should include secure use of Microsoft Teams, Slack, and other collaboration platforms, since attackers often exploit cross-platform weaknesses or leverage compromised accounts to escalate attacks beyond email.
- Zero Trust Culture: Modern programs are embedding “never trust, always verify” principles at every endpoint. This means every unexpected request, whether it’s a new vendor payment or a change to payroll, requires additional authentication, regardless of how legitimate the sender appears.
- Continuous, Automated Reinforcement: Automated reminders about suspicious activity, clickable simulations embedded in real emails, and interactive push notifications help keep users alert. These micro-interventions, supported by quality analytics, can drive down risky behaviors over time.
Following these trends demonstrates a proactive approach to email cybersecurity and compliance, protecting your business from emerging risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Attackers increasingly use spear-phishing, business email compromise, and threats that mimic trusted contacts or regular processes. Many basic programs don’t prepare employees for highly personalized messages or urgent financial requests forged to appear as internal communications.
Organizations should update their training at least quarterly. However, any time a new attack method or regulatory requirement emerges, immediate refreshers or alerts should be issued to all users.
Secure email hosting with end-to-end encryption, AI-driven threat detection, multi-factor authentication, advanced filtering, and robust quarantine policies are recommended. Integrating these with regular user training creates multiple layers of defense.
Foster a positive atmosphere by rewarding or recognizing staff who report potential threats. Remove blame from the process, focus on learning outcomes, and ensure employees know that prompt reporting is valued over perfection.
External experts bring advanced tools, current intelligence, regulatory experience, and fresh perspectives, helping in-house teams identify blind spots and build more resilient, sector-specific training and technology solutions. Their knowledge of local and industry-specific risks ensures customized, practical protection.