Identifying Hidden Risks Behind Secure Email Hosting Promises
Businesses rely on digital communication every day, but email remains a favorite entry point for cybercriminals. While most companies use secure email hosting solutions to guard sensitive data, too many assume that standard features equal total protection. That trust can be misplaced. Even reputable email security vendors may have blind spots in their designs, implementation, or support models. This reality poses challenges for organizations across New Jersey and beyond, particularly in regulated industries where compliance lapses can be dire.
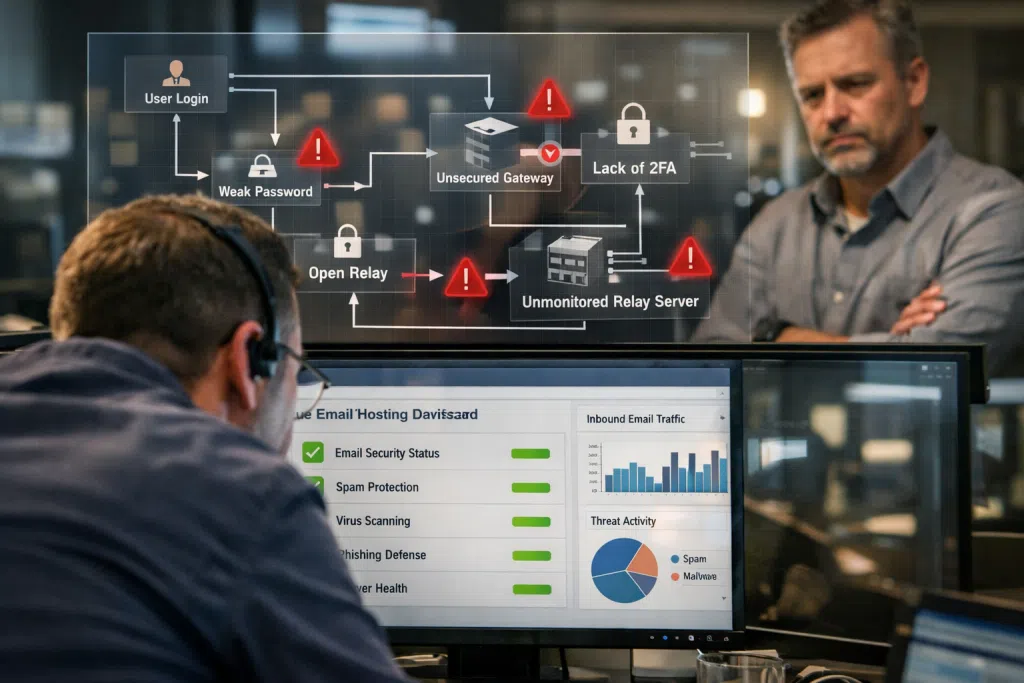
Transmitting business-critical information, legal files, financial records, or patient data via email exposes organizations to threats like phishing, business email compromise, data loss, and reputational damage. Secure mail hosting is marketed as a solution, but not all providers deliver equally on their promises. Email server security failures rarely announce themselves until a breach hits.
Recognizing the risks is only part of the solution. You must ask the right questions, examine your vendor’s true capabilities, and spot warning signs of coverage gaps. These shortfalls may include outdated encryption, inconsistent patching, vulnerable server configurations, lax compliance controls, lackluster incident response, or limited advanced email security features against evolving threats.
Leadership teams should not leave these issues to technical staff alone. Regulators, clients, and insurance carriers expect executive buy-in and oversight. Failure to secure business email costs U.S. firms billions annually, according to the FBI’s 2026 Internet Crime Report, with business email compromise remaining one of the most lucrative attack techniques.
How do you know if your email protection services meet your industry’s security standards? Is your provider transparent about their infrastructure, certifications, or monitoring approach, or do they deflect or confuse critical questions? Many organizations only find out after an incident that their supposedly secure email hosting solution had critical vulnerabilities or compliance gaps.
Connect with Blueclone Networks now to get a clear assessment of your email security posture and see if your provider’s promises translate to genuine protection.
What Sets Truly Secure Email Hosting Apart From Bare-Minimum Service
It’s easy for vendors to advertise email protection services and claim industry-standard safeguards. But digging deeper, leading secure mail hosting providers invest in multilayered controls, not just basic encryption in transit or anti-spam filtering. For organizations facing regulatory scrutiny, the differences between bare-minimum, checkbox solutions and comprehensive email protection are stark, sometimes catastrophic.
Key Elements That Distinguish Robust Secure Email Hosting:
Proactive Threat Detection and Evolving Controls
Legacy spam filters and static rules no longer cut it. Modern threats use sophisticated deception, compromised supply chains, and zero-day exploits to bypass basic barriers. Effective vendors deploy advanced email security, including behavioral threat detection engines, machine learning models for anomaly spotting, and reputation-based blacklists that update hourly. Protection must adapt as quickly as threats change.
Strong Encryption At Every Stage
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is standard, but what about message-level or end-to-end encryption for confidential correspondence? Enterprise-grade solutions offer encrypted storage, encrypted backups, and intricate key management. This matters for sectors like healthcare, finance, and legal, where sensitive attachments and records require stringent data controls beyond just “encrypted in motion.”
Granular Administrative Controls and Auditing
Can you enforce role-based access to mailboxes, apply multifactor authentication (MFA) to admin panels, or restrict login locations? Can you review immutable audit logs for mailbox access or email forwarding activity? Best-in-class email security vendors build granular controls for compliance and internal investigations. Lack of detailed auditing often signals a less mature provider.
Automated Response and Threat Remediation
Today’s business email attacks are fast-moving. A single phishing email can trigger credential theft or ransomware within minutes. Established vendors integrate automated quarantine, instant user lockout, and real-time rollback of malicious changes. These features minimize the impact of the window and support disaster recovery.
Up-to-Date Compliance Alignment
For regulated businesses, your secure email hosting should support not just HIPAA or PCI-DSS compliance, but ongoing changes in state, federal, and even global requirements. Reliable providers help you prepare for audits, maintain evidence, and respond to new regulatory updates, rather than playing catch-up after rules change.
Transparent Third-Party Assessments and Certifications
Does your provider engage independent cybersecurity auditors? Are their SOC 2 reports, penetration testing records, or certification status readily available? Beware vendors unwilling to share external validation or those whose documentation falls years out of date.
Organizational leaders, especially in central New Jersey’s finance, healthcare, or legal sectors, should expect these features as a baseline. Anything less leaves entire categories of attacks unmitigated. Don’t be content with only a “good enough” approach, especially when both compliance and reputation are on the line.
Uncovering the Most Common Gaps in Email Server Security
Without rigorous attention, vulnerable configurations and overlooked details can erode even top-tier email security. These common gaps appear in legacy, cloud-hosted, and even so-called “secure mail hosting” environments:
1. Misconfigured SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Records
Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) are foundational tools. Yet, according to an analysis published by CSO Online in March 2026, over 50% of SMB domains in North America have incomplete or absent DMARC records, leaving them susceptible to email spoofing and impersonation.
2. Lagging Patch Management
Outdated server operating systems, web interfaces, and even third-party plugins are favorite targets for attackers. Unpatched vulnerabilities enable privilege escalation or unauthorized mailbox access. Regular patch schedules and vulnerability scans are a must, if your provider cannot document or automate their update policy, critical exposures may linger.
3. Weak User Access Controls
Too often, former employees retain access, or generic administrative mailboxes lack multifactor authentication. Secure email hosting vendors should offer granular, automated user provisioning and revocation, with reporting to confirm idle accounts or advanced threat monitoring for high-privilege logins.
4. Inadequate Endpoint Security Integration
Email server security doesn’t live in isolation. If endpoints, laptops, mobile devices, and shared workstations can be compromised, malware may auto-forward sensitive email content outside your control. True leaders in advanced email security integrate with endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, mobile device management (MDM), and secure containerization options for bring-your-own-device (BYOD) scenarios.
5. Insufficient Backup and Incident Restoration
The FBI and CISA have noted that ransomware and data-destructive attacks have increased in speed and complexity throughout 2026. Is your hosted email protected with real-time, granular backups and rapid restoration capabilities? Many low-cost vendors rely on slow, incomplete restore options that can cripple business during an incident.
6. Limited Phishing Simulation and Security Awareness Training
Top-tier providers offer more than raw technology. Ongoing security awareness campaigns, like simulated phishing attacks and interactive training, help employees spot threats and respond correctly. Without these, even the most advanced technical safeguards may be bypassed by simple human error.
7. Incomplete Regulatory Readiness
Especially in New Jersey’s regulated sectors, compliance is not a one-time checkbox. Regular audits, evolving IM/IT policy requirements, and new laws demand that your vendor stay ahead and can prove it. Lacking up-to-date compliance documentation or responsive legal support leaves organizations exposed.
These represent only the most common points of failure. Constant diligence, frequent reviews, and a robust partnership with your secure email hosting vendor are essential for maintaining trust and ensuring nothing slips through the cracks.
How Advanced Email Security Tools Defend Against Modern Attacks
Hackers do not use yesterday’s playbook. According to a recent Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (2026), social engineering, credential harvesting, and account takeover continue to trend upward. Standard email hosting simply cannot keep up. To counter these dangers, modern organizations turn to advanced email security capabilities that go far beyond old-school filters and spam folders.
Machine Learning–Driven Anomaly Detection:
Today’s advanced email security systems build baseline profiles of normal sender, recipient, and content behavior. If a message deviates from these norms, such as login from a suspicious foreign IP, or an unexpected funds transfer request, it’s flagged or blocked automatically. These reactions occur in real time, speeding up response and preventing widespread compromise.
Attachment and Link Sandboxing:
Zero-day malware and ransomware payloads are engineered to evade conventional scans. Sandboxing isolates suspicious attachments and links, executing them in controlled environments to observe their behavior. If malicious, these emails are held, analyzed, and reported to administrators before harm is done.
Integrated Threat Intelligence:
The best email security vendors utilize live threat feeds, blacklists, and crowd-sourced malware intelligence. Real-time integration helps detect phishing links, newly registered attacker-controlled domains, or emerging attacker techniques before they can impact inboxes. According to Gartner’s Top Security Trends for 2026, intelligence-driven security tools correlate events across millions of global endpoints to pinpoint threats ahead of time.
Email Authentication Analysis:
As discussed earlier, email authentication protocols, including DMARC, are critical safeguards. But enforcement is not set-it-and-forget-it. Leading providers regularly review authentication logs, generate detailed reports, and adjust policies to match new business partners and workflow changes. This reduces successful spoofing and domain impersonation.
Automated Quarantining and Incident Response:
When a modern attack is detected, immediate action is vital. Advanced tools automatically quarantine malicious emails, alert IT staff, and can even lock compromised accounts until a proper review is done. Automation shrinks response times and contains threats before data is lost.
User and Executive Protection:
Targeted phishing, sometimes called “whaling”, aims to trick leadership into fraudulent wire transfers or disclosing sensitive data. Executive-specific protection layers recognize these attempts and enforce extra scrutiny, including secondary verification and direct communication with the intended sender.
Detailed Reporting for Audit and Compliance:
In regulated industries, logs, incident metrics, and detailed compliance reports are a necessity. Advanced solutions automate the collation, storage, and presentation of these materials to prepare for both external audits and internal reviews.
Connect with Blueclone Networks now to see how advanced email security can shield your staff and clients.
Questions Every Business Should Ask Its Email Security Vendors
Choosing a vendor for secure mail hosting isn’t about chasing the lowest price or the flashiest interface. For organizations worried about data loss or compliance fines, rigorous vendor due diligence is non-negotiable. An effective question set can reveal whether your provider is truly built for modern business risks.
What Encryption Standards Are Used?
Ask for precise details: Are AES-256 encryption algorithms enforced both during transmission and at rest? Can they prove end-to-end encryption is available for sensitive workflows?
How Frequently Are Security Updates and Patches Applied?
Find out about their patch management process. Is patching automated and timely? Can they document their process for rapid vulnerability response to critical exploits discovered in the wild?
Are Multifactor Authentication and Geo-Restriction Available on All Accounts?
Insist on MFA not just for admin access, but for all user accounts, and for the ability to restrict logins by geographic region or device profile.
Can You Provide Third-Party Audit Results or Certifications?
Trustworthy vendors will share up-to-date audit documentation, SOC 2 reports, penetration testing summaries, or other independent reviews. If they hesitate or provide only outdated reports, push for more.
How Do You Handle and Notify About Security Incidents?
Request a walk-through of their incident response plan. How quickly are clients notified of a breach? Are there automated containment options? How is forensic data preserved?
What Options Exist for Advanced Threat Protection, Phishing Simulation, and Security Awareness Training?
Best-in-class vendors include or support human-focused security features. Training and simulations help staff stay alert for evolving attacks and boost overall security posture.
Can You Support Our Compliance Needs (HIPAA, FINRA, PCI-DSS, Etc.)?
For regulated industries, generic “secure hosting” is not enough. The provider should document their compliance program, offer audit support, and deliver regulatory alignment for your industry.
What Happens If a User Account or Server Is Compromised?
Clarify steps for account isolation, backup restoration, and client notification. Failover capabilities and detailed, tested playbooks should be ready to share and review.
Is Threat Monitoring in Real-Time, and What Is the Scope?
Does the provider deliver true 24/7 monitoring via a staffed SOC or automated alerting platform? Is monitoring performed on all message types, endpoints, and integrations?
How Are Backups Managed and Protected?
Understand how often backups are created, where they are stored, and the policy for restoring data. Backups must be encrypted, immutable, and quickly accessible in a crisis.
Vendor transparency in answering these questions signals commitment to your security, not just to their own margins.
Bringing Your Secure Email Hosting up to Date: A Checklist for Business Leaders
Keeping your organization protected means more than just running antivirus on endpoints. Email server security relies on holistic, coordinated controls and constant vigilance, much of which starts at the leadership level.
Business Leader Secure Email Hosting Checklist:
- Review Your Current Provider’s Feature Set: Map your current environment against the advanced controls discussed. If you’re missing automated threat detection or robust auditing, request upgrades or consider alternatives.
- Conduct a Security Posture Assessment: Engage experts to run a security review and penetration test specifically targeting your hosted email solution.
- Gap Analysis vs. Regulatory Requirements: Compare your secure mail hosting environment with specific rules that govern your sector, such as HIPAA, FINRA, or PCI-DSS, the cost of noncompliance can run much higher than the price of a security upgrade.
- Implement MFA Across All Access Points: Mandate multifactor authentication for everyone, including contractors and third-party vendors who might access your mail environment.
- Roll Out Security Training and Simulations: Encourage regular phishing simulations and awareness sessions; people remain the first and last line of defense.
- Verify Patch Management and Vulnerability Scanning: Ask for proof of schedule and recent patch reports. Outdated software is a common vector for high-impact breaches.
- Demand Transparent Reporting and Audit Support: Ensure your provider can generate compliance-aligned reports and is willing to participate in your organization’s reviews.
- Plan for Breach Response and Restoration: Understand, document, and periodically test your provider’s incident response and disaster recovery capabilities.
According to the Ponemon Institute’s 2026 Cost of a Data Breach Report, businesses with strong security training, automated detection, and comprehensive backup/disaster recovery pay $1.4 million less per incident on average. Implementing even a few checklist items can elevate your organization’s defenses dramatically.
Connect with Blueclone Networks now to ensure your email security stack is built for tomorrow’s threats, not yesterday’s.
FAQ: Secure Email Hosting, Security Gaps, and What Your Business Needs to Know
A provider that avoids giving technical documentation, delays patching, cannot produce current certifications, or fails to offer advanced threat protection is likely leaving you exposed to risks.
Secure mail hosting includes stronger encryption, advanced threat detection, comprehensive backup, granular user controls, and certified compliance support. Standard email hosting rarely meets these thresholds, especially for regulated businesses.
No solution is infallible. Even large, reputable vendors must actively maintain, assess, and upgrade protections. Regular third-party audits, transparent architecture, and up-to-date threat intelligence are more important than brand recognition alone.
These authentication protocols prevent email spoofing and domain impersonation. Without them, attackers can send messages that appear to come from your organization, tricking staff and clients.
Regular assessments, quarterly or after any major incident, software update, or regulatory change, help ensure that your environment adapts to evolving threats and maintains compliance.