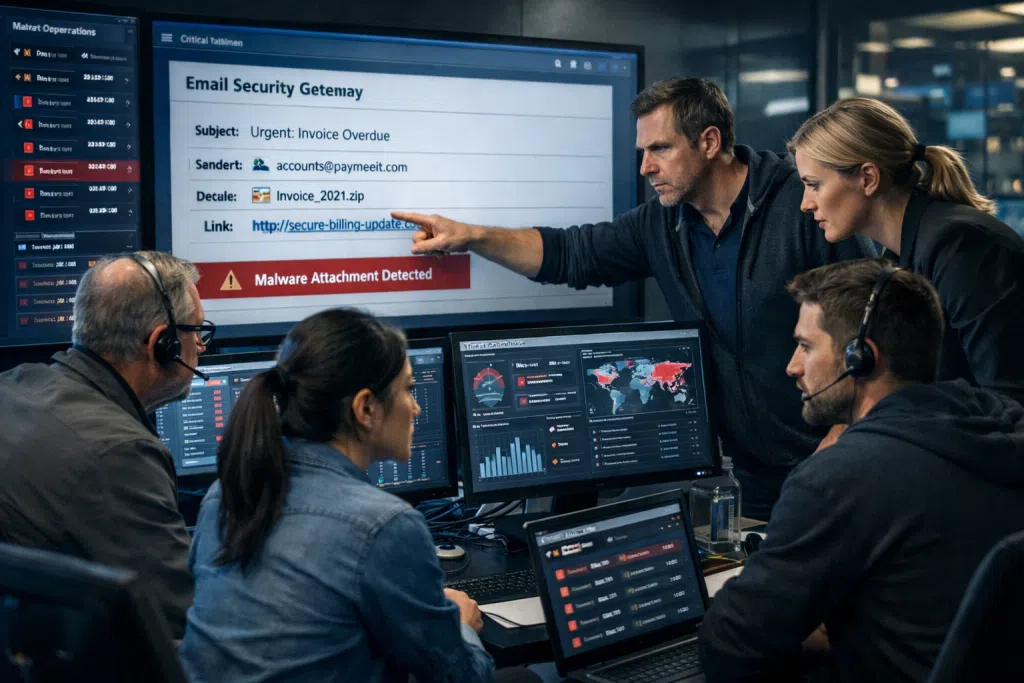
Unseen Risks Lurking Behind Traditional Email Security Gateways
Despite heavy investments in email security gateways, many businesses across New Jersey and the Tri-State area continue to face costly breaches due to advanced phishing, business email compromise, and credential theft. Cybercriminals constantly devise new attack techniques specifically designed to slip through layered defenses, placing organizations, especially small and mid-sized firms in regulated sectors, at outsized risk. Simply having an email security gateway is not enough in 2025, given the escalating arms race between attackers and defenders.
Email remains the primary route for malware, ransomware, and credential harvesting attacks. Even with spam filters, signature-based detection, and legacy secure email policies, emails carrying zero-day payloads or well-crafted social engineering ploys frequently bypass existing controls. Attacks are often disguised within legitimate-looking business correspondence or made to appear as trusted contacts. For healthcare and financial organizations beholden to HIPAA, FINRA, or PCI-DSS, the consequences extend beyond immediate financial loss to potential regulatory penalties and long-term reputation damage.
In fact, recent research from the 2026 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report reveals that email phishing is implicated in over 80% of organizational breaches, with average remediation costs now reaching upwards of $4.45 million globally IBM, 2026. For local firms handling sensitive patient or client data, this dynamic reinforces the critical need for advanced detection strategies that move beyond what standard gateways offer.
Unlike the predictable spam of years past, today’s threats blend social engineering, AI-powered mimicking, and tailored payloads. Attackers exploit loopholes in email server security, attempt to predict employee behavior, and leverage compromised vendor accounts, a phenomenon known as supply chain email compromise. Business leaders and IT directors in Princeton, Trenton, and throughout Central NJ should be asking: Are we protected against the latest generation of threats, or trusting gateways that are already outdated?
A truly secure email environment demands not just bolt-on filtering but a proactive, layered defense: one that incorporates intelligent behavioral analysis, real-time threat updates, advanced sandboxing, and continuous training of end-users. The time to reassess your organization’s email security policy and defenses is now. Connect with Blueclone Networks now to discuss solutions built for today’s evolving threat landscape: Book a consultation here.
Why Standard Email Security Gets Outsmarted by Modern Attacks
Many SMB owners and IT departments remain confident in their email security gateway investments, only to discover too late that these platforms miss the majority of cleverly disguised attacks. Traditional gateways, although essential, were originally built to detect spam, mass phishing, or attachments with known malicious code. In reality, offensive tactics have evolved far more rapidly than many of these tools can keep pace.
Modern attackers understand exactly how signature-based filtering, rules-based scanning, and basic blacklists work. They craft messages with unique or never-seen-before elements, often using AI to convincingly spoof executive emails or trusted vendors, and update payloads frequently to avoid known reputation lists. Some of the most dangerous emails carry no attachments or obvious links, instead deploying fileless malware using trusted Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace features, or tricking employees into logging credentials on mirrored login portals.
For example, a surge in business email compromise (BEC) has been observed in the legal and finance sector, where attackers will monitor communications to insert themselves at critical points, like during wire transfer authorizations or client onboarding. Email security gateways, especially those with limited behavioral analysis, rarely flag these “in-context” emails. Similarly, hospitals in NJ have been targeted by emails that appear to originate from legitimate medical suppliers or regulators, bypassing traditional gateway scoring by exploiting trust.
Cloud email security tools offer improved efficacy, but also come with unique risks. Cybercriminals now design attacks to exploit weaknesses in OAuth permissions, MFA fatigue, or misconfigured cloud settings. Without ongoing risk assessments and adaptive policy enforcement, even best-in-class gateways can provide a false sense of confidence. The need for advanced email security, tailored for the compliance and attack patterns of your industry, has never been more urgent.
Emerging research highlights the importance of layered defense. According to Verizon’s 2026 Data Breach Investigations Report, over 68% of successful phishing attacks that bypassed initial security caught organizations “off guard,” often due to assumptions that their gateway would catch all threats. These incidents reinforce a critical lesson: static defenses are no match for adaptive, persistent adversaries.
Evolving Tactics: How Threat Actors Bypass Advanced Defenses
Cybercriminals now employ a blend of tactics specifically engineered to defeat even the most advanced email security gateways. Social engineering has matured: phishing lures are tailored, context-specific, and often built upon public data harvested from professional directories or social networking sites. In regulated industries such as healthcare and finance, attackers mimic internal communication styles, use authentic-looking logos, and reference current projects to increase success rates.
A prevalent tactic involves account compromise, gaining control of an employee’s cloud email account, and launching attacks from within. This allows malicious actors to sidestep external gateway scrutiny, as messages arrive from a “trusted” source. Once inside, they often exfiltrate sensitive files, manipulate payment instructions, or escalate privileges. Many businesses discover these breaches days or weeks after initial compromise, often during a forensic review prompted by a regulatory inquiry.
Forward-thinking adversaries also weaponize file-sharing services and cloud storage links, knowing that secure email systems may whitelist organizational domains but not scan deeply for obfuscated threats. Multi-stage attacks are now the norm, where the initial message, appearing innocuous, delivers the actual payload through a second communication or an external trigger.
Other sophisticated methods include:
- Zero-day exploits: Where attacks leverage brand new, unpatched vulnerabilities before security vendors update detection signatures.
- Timeout phishing: Using MFA fatigue or time-limited authentication requests to rush employees into sharing credentials.
- QR code phishing (quishing): Disguising malicious URLs in QR codes that, when scanned, bypass gateway link analysis.
Attacks targeting SMBs often exploit gaps in email server security, particularly in smaller firms with limited in-house security staffing. Legal practices and medical offices have been tricked by fake requests for wire transfers or updates to billing details, resulting in tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars in losses.
Complicating matters further, emerging threats blend AI-generated text with spoofed executive identities, making phishing claims harder to flag through traditional keyword or pattern detection. Without adaptive, machine-learning-driven security layers and regular staff training, businesses will continue to fall victim to these evolving strategies.
This environment demands an agile response. Legacy secure email systems must be paired with advanced detection, forensic monitoring, and policy-driven controls if they’re to provide real-world protection against the diverse threat landscape targeting NJ businesses.
The Essential Components of Advanced Email Security in 2025
Recognizing the limits of outmoded technologies, organizations are now embracing a layered approach to advanced email security. The most effective strategies combine a modern email security gateway with innovative detection methods, leveraging AI for real-time insights and integrating proactive protections directly at the email server and user level.
Key elements of an advanced, enterprise-ready secure email solution include:
- Behavior-Based Threat Detection: Instead of relying solely on static rules or reputation lists, modern solutions analyze message content, sender history, and user behavior, flagging anomalies such as suspicious login times, unfamiliar device access, or sudden changes in message volume.
- Real-Time URL and Attachment Sandboxing: All incoming links and files are executed within a safe, isolated environment before reaching user inboxes. This allows zero-day malware and unknown exploits to be detected based on behavior, not just signatures.
- API-Level Cloud Email Security: Integrating directly with Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and other cloud providers, these tools monitor for account compromise, data exfiltration, and malicious third-party OAuth grants, providing a vital layer for co-managed IT departments.
- AI-Driven Phishing Detection: Artificial intelligence models now learn from organization-specific communication patterns. This allows detection of nuanced phishing: emails written in a specific executive’s style or referencing current events unique to the business.
- Continuous Security Awareness Training: Employees are regularly tested with simulated phishing campaigns and educated about new tactics. Research consistently shows that trained staff are the last, and often the most effective, line of defense.
- Automated Incident Response and Quarantine: Suspected messages are automatically quarantined, and users are alerted instantly. Policy-driven actions allow IT to respond at machine speed, reducing the potential for human error.
- Auditable, Regulatory-Focused Email Security Policy Enforcement: Not only do advanced email security solutions block malicious messages, but they also enforce data retention, email encryption, and archiving policy requirements, essential for HIPAA, FINRA, or PCI-DSS compliance.
Case in point: A Princeton-based healthcare group recently avoided a compliance breach because its email security policy included end-to-end encryption and AI detection quarantine. A targeted credential phishing attempt, which bypassed their legacy gateway, was intercepted and isolated by the advanced system before any staff engaged.
Incorporating these technologies does not require a “rip and replace” of existing infrastructure. Many cloud email security providers now offer modular, API-based overlays that extend current platforms, improving protection without disrupting workflow. For regulated SMBs, this stratified model delivers improved defense while ensuring alignment with legal and industry-specific mandates.
If you’re concerned about gaps in your email security or want to benchmark your defenses against modern threats, connect with Blueclone Networks now to discuss a tailored, compliance-centric solution: Book a free assessment.
Strengthening Cloud and On-Premise Email Server Security
Many Central NJ businesses rely on both cloud-based systems, like Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace, and traditional on-premise email servers. Each approach presents its own blend of benefits and risk profiles. While cloud platforms offer rapid patching and built-in redundancy, misconfiguration or lax permissions create vulnerabilities. On-premise servers may be within your direct control but require constant updates and expert oversight to avoid falling behind on security posture.
Key practices to improve email server security, regardless of deployment model, include:
- Enforce Strong Authentication Mechanisms: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be mandatory for all email access, both web-based and client (Outlook, Thunderbird, etc.), and regularly tested for effectiveness against new attacks like MFA push fatigue.
- Apply the Principle of Least Privilege: Limit user access based on role, and regularly audit group permissions to minimize internal attack surface.
- Automated Patch Management: Both cloud and traditional servers demand continuous updates for all components: operating system, mail transport agent, anti-malware plugins, and web-facing interfaces. Most recent exploits, like ProxyNotShell or ZeroLogon, have targeted outdated installs.
- Email Flow Encryption: TLS or better should be enforced for all internal and external server-to-server communications, with fallback disabled to prevent downgrade attacks.
- Monitoring and Rapid Event Response: Deploy continuous logging and SIEM integration to surface suspicious authentication, outbound spam spikes, or brute-force attempts early.
- Backup and Recovery for Email Data: Even robust, secure email setups can be undermined by ransomware or accidental deletion. Ensure that both cloud and on-premise platforms have third-party, immutable backup, separate from production systems, to guarantee recoverability without paying a ransom.
For co-managed IT environments, where partial control resides with both in-house and external teams, consider implementing shared dashboards and clearly defined runbooks for incident response. This transparency allows for faster, coordinated responses to email-borne threats, fulfilling audit and compliance requirements for sectors such as legal, healthcare, and finance.
A pharmaceutical firm in New Jersey recently reinforced their defenses by migrating legacy Exchange servers to a hybrid model, pairing Blueclone’s cloud email security with robust on-premise policy controls. This layered method delivered both operational agility and improved auditing, reducing risk exposure to targeted attacks.
Given the hybrid and constantly shifting nature of email ecosystems, periodic security reviews are essential. Providers with regional expertise, regulatory insight, and multi-environment capability, like Blueclone Networks, can help bridge the gap between compliance and security effectiveness.
Building and Enforcing a Resilient Email Security Policy
Regulatory demands and the threat landscape compel New Jersey businesses, especially within healthcare, financial, and legal sectors, to have an up-to-date, actionable email security policy that is more than just documentation. A truly effective policy guides day-to-day operations, response actions, and ongoing risk management.
Crucial elements for a modern email security policy:
Defined Roles and Responsibilities
Clarify ownership of various email security controls, from incident detection to end-user reporting. For co-managed IT, this means specific lines of decision-making between internal staff and MSP partners.
Acceptable Use and Data Handling Protocols
Specify how employees interact with sensitive or regulated information via email, including use of encrypted communications, classification of PHI or PII, and protocols for sending to external parties.
Attachment and Link Controls
Include standardized procedures for handling unexpected attachments, unsolicited document-sharing links, or requests for credential confirmation, paired with mandatory reporting.
Required Email Security Gateway Features
Mandate that all email systems use advanced filtering, AI-powered detection, and continuous sandboxing. Stipulate automated quarantine and clear escalation paths for suspected threats.
Regular Policy Review and Update Cycles
Cyber risk evolves daily. The email security policy must undergo scheduled updates, prompted by either regulatory changes or new types of attacks, with version-control and cross-departmental participation.
Security Awareness Training Mandate
Make simulated phishing exercises and user awareness training a requirement for all staff who have access to business email. Track participation and improvements as a metric of organizational risk.
Incident Response Process
Include step-by-step actions for suspected compromise: from initial user alert, to isolation, to forensic review, and required reporting to legal or regulatory bodies. Link this process directly to the larger business continuity plan.
These guidelines should not be treated as a formality. For example, a Somerset, NJ law office strengthened its position in a 2023 lawsuit concerning wire fraud by demonstrating a clear, enforced policy that included rapid notification procedures. Their preparedness lessened regulatory scrutiny and preserved client trust, outcomes unattainable with only technical solutions.
It’s especially important for SMBs in regulated fields to treat email security policy as a living document. Aligning policy with daily practice, leveraging cloud email security, and prioritizing continuous education create an environment where employees are active participants in protection, not the weakest link.
For organizations ready to review their own policies or implement technical controls, the path forward is best navigated with experienced partners. Connect with Blueclone Networks now for a policy review or compliance-focused security assessment: Schedule a consultation here.
FAQ: Email Security Gateway and Advanced Threat Protection
An email security gateway is a solution designed to filter out unwanted emails, detect phishing attempts, and block malware before they reach inboxes. It acts as the first line of defense by scanning inbound and outbound messages based on rules, signatures, and basic behavioral analysis. For businesses handling client, patient, or financial data, a security gateway helps reduce exposure to common cyber-attacks and meets basic compliance requirements. However, with attackers using AI-driven and context-specific threats, relying solely on a gateway is not enough for comprehensive protection.
Cybercriminals use methods that exploit human trust and organizational workflows. They design emails that mimic real conversations, compromise trusted accounts, use fileless malware, insert malicious links in common file-sharing services, and employ techniques like QR code phishing. Some attacks are customized to the target, making them hard for static rule-based systems to detect. To counter these, organizations require layered defenses, behavior-based monitoring, and employee training.
Cloud email security solutions integrate with platforms such as Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace, offering real-time updates, AI-driven detection, and adaptive policy enforcement. They are generally more responsive to emerging threats and easier to update than on-premise appliances. However, both deployment models have unique vulnerabilities. The most effective approach is a hybrid or overlay model where advanced cloud-based protections support or supplement legacy gateways.
Security awareness training is essential because users often represent both the strongest and weakest point in your defenses. Regular training with simulated phishing scenarios helps staff recognize suspicious messages, reduces the likelihood of successful social engineering, and ensures compliance with internal email security policy guidelines. Well-trained employees can spot subtle attacks that bypass technical filters.
Blueclone Networks brings specialized experience serving SMBs in regulated sectors across NJ, Eastern PA, and NYC Metro. Their team provides advanced email security, policy development, co-managed IT solutions, and user training tailored to compliance frameworks like HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and FINRA. From risk assessments and cloud integration to rapid incident response, Blueclone supports organizations with both technical and procedural measures designed to meet the evolving threat landscape and regulatory mandates.