Email Server Security: Why It’s No Longer Optional for Modern Businesses
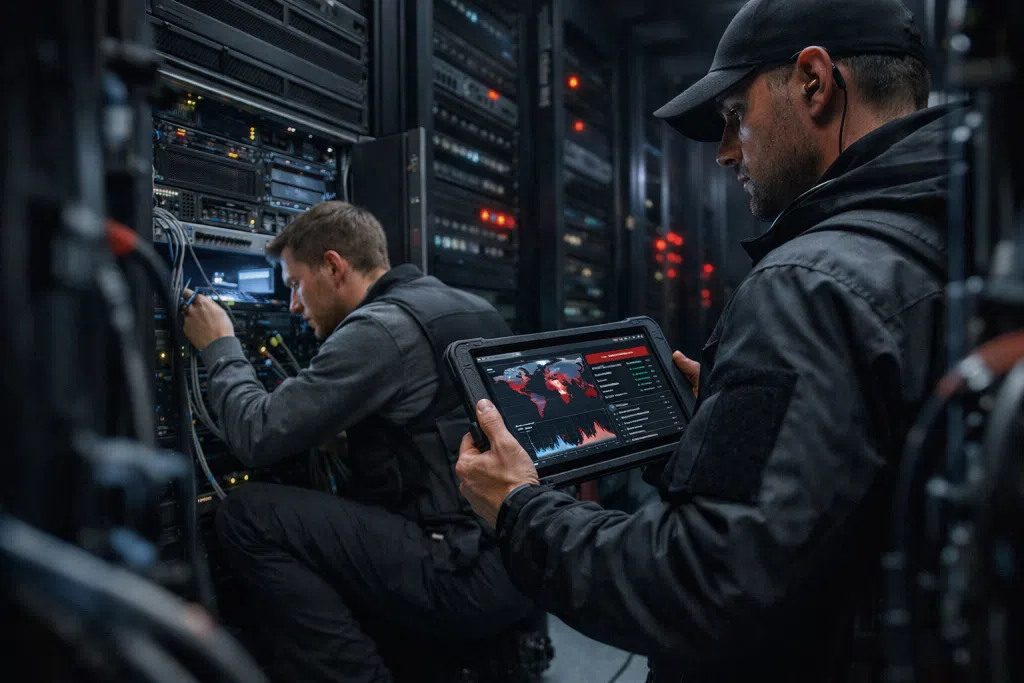
Email remains the lifeblood of business communication. Yet, as indispensable as email is, it’s also a favorite target for cybercriminals. Each year, organizations across New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and New York City witness evolving tactics, from sophisticated phishing schemes to multi-stage ransomware campaigns, testing the resilience of their email server security. For regulated sectors like healthcare, finance, law, and life sciences, the stakes are even higher. A single breach can result in financial loss, loss of client trust, and regulatory consequences.
Effective email server security is far more than ticking boxes for compliance audits. It is a continuous commitment to protecting sensitive business data, complying with industry requirements, and maintaining operational continuity. The numbers paint a clear story: according to the FBI’s Internet Crime Report 2026, business email compromise (BEC) led to estimated losses surpassing $2.2 billion in just one year, with small and mid-sized firms hit hardest.
So, what exactly puts your communication infrastructure at risk? Many organizations still rely on outdated email security, seeing their mail servers as IT maintenance chores rather than essential business assets. Others assume that default protections included with email platforms are “good enough.” In reality, advanced email security threats bypass basic filters using multi-vector attacks, social engineering, and even artificial intelligence. Hackers exploit vulnerabilities in legacy systems, unpatched software, or human error.
Despite evolving risks, the solution isn’t simply to add another tool or complicated gateway. It requires a holistic approach: robust protocols, continuous user education, hardened secure mail hosting, superior authentication controls, and specialized monitoring tailored to your risk profile.
Philadelphia and New Jersey firms, especially in regulated environments, cannot afford to treat email server security as an afterthought. This is where a proactive review of your current defenses, including beyond-the-basics email protection services, becomes crucial. If you’re unsure about the strength or completeness of your current defenses, it’s time for a professional assessment.
Connect with Blueclone Networks now for a thorough evaluation and actionable improvements that fit your business realities.
Understanding the Most Common and Emerging Email Security Threats
Email server security must evolve as cybercriminals refine their attacks. Gone are the days when spam and basic phishing made up the bulk of email threats. Today, adversaries deploy multifaceted attacks that can pierce even apparently strong defenses.
Phishing Remains Prevalent, but Far More Sophisticated
Modern phishing campaigns mimic legitimate communications better than ever. Attackers invest time researching victims, often using social media and breached data dumps to create plausible sender addresses and content. CFOs, attorneys, and healthcare administrators in Central NJ are commonly impersonated by threat actors in targeted spear-phishing campaigns. One click on a malicious link can compromise the entire network, opening the door for financial theft, data breaches, or ransomware.
Business Email Compromise (BEC) on the Rise
BEC attacks have become a signature weapon, particularly against SMBs. Fraudsters infiltrate or spoof company email accounts and trick staff into sending payments or divulging confidential information. According to the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), BEC losses have eclipsed most other forms of email-centered crime, largely due to attackers’ precision and patience. They may wait weeks or months after gaining access before striking.
Ransomware and Malware Delivery
Emails remain the number one vector for ransomware distribution. Cybercriminals attach infected documents or embed links to rogue websites. Advanced email security solutions can help screen out known malicious attachments, but modern ransomware often uses encrypted attachments or fileless tactics to avoid detection.
Emergence of Deepfake and AI-Generated Email Attacks
AI-generated content and deepfake technologies are now being used to construct emails that are almost indistinguishable from genuine business messages. Employees are confronted with fake invoices, HR requests, or legal correspondence that sound authentic in tone, adding another layer of difficulty to detection.
Supply Chain and Vendor Impersonation
A breach in an external business partner’s email security can quickly impact your own operations. Attackers impersonate trusted suppliers or even regulators (such as FINRA or the FDA), inserting themselves into existing conversations. These attacks can bypass ordinary email protection services by relying on a chain of trust and familiarity.
Zero-Day and Fileless Attacks
Traditional antivirus and legacy email security gateway appliances regularly miss zero-day threats or fileless malware. These often rely on exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities in mail servers or embedded scripting within emails.
For organizations intent on protecting both communications and client confidentiality, understanding these threat vectors is crucial. Reviewing incident reports from your security vendor or recent FBI cybersecurity updates can inform an evolving defense posture.
Building a Layered Defense: Key Elements of Advanced Email Security
A true modern email security strategy must go far beyond basic filtering and antivirus. Building defenses that are multi-tiered protects against known risks and emerging threats. Here’s how organizations across New Jersey, especially those subjected to HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or financial regulatory requirements, should structure their approach:
Secure Mail Hosting with Built-In Encryption
Choose email hosting providers whose platforms offer robust encryption both at rest and during transmission (using TLS and advanced S/MIME protocols). This means that if email messages are intercepted, they offer no value to attackers. Encryption is not just a best practice for sensitive industries; it’s now expected under most U.S. and international compliance frameworks.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Is Essential
Weak or compromised passwords account for a large share of unauthorized mailbox access. Multi-factor authentication makes it nearly impossible for an attacker to gain entry using just stolen credentials. Mandating MFA across all users, including C-suite executives and IT administrators, should be non-negotiable.
Advanced Threat Detection and Sandboxing
Modern secure mail hosting utilizes advanced detection engines and “sandboxing.” Unknown or suspicious attachments are opened in controlled environments, away from your production network, to screen for malicious behavior. These tools supply real-time updates to block zero-day ransomware and never-before-seen phishing templates.
Email Security Gateways: Sophistication Over Simplicity
Email security gateways now need to offer more than just spam filtering. The best products include sender policy framework (SPF), domain keys identified mail (DKIM), and domain-based message authentication, reporting, and conformance (DMARC) policies. Together, these prevent attackers from spoofing your domain and tricking recipients.
Email security gateways also offer advanced phishing protection, real-time URL scanning, and threat intelligence feeds that provide protection against evolving attack vectors. Look for solutions that integrate with your existing cloud services (like Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace) without causing latency or bounce issues.
User Awareness and Recurring Training
Technology alone can’t solve every problem. Staff who don’t recognize advanced phishing or social engineering will always be vulnerable. Effective training programs that recur quarterly boost your email security posture. New hires should also be trained before given access to sensitive communications.
Outbound and Inbound Message Inspection
A layered approach checks both incoming and outgoing messages. Outbound filtering helps prevent sensitive data leaks (socket-layer data loss prevention, or DLP), either accidentally or as a result of compromise.
Each of these pillars works together to reduce risk. The right balance of managed services, automated tools, and human oversight can help businesses across healthcare, law, finance, and professional services defend their most critical communication channel.
Connect with Blueclone Networks now to discover customizable defense strategies designed for your business.
The Role of Professional Email Protection Services in NJ’s Regulated Markets
Professional email protection services are no longer optional, especially for organizations dealing with protected health information (PHI), client legal records, or financial data. The compliance environment in New Jersey and the broader Northeast demands IT partners with both technical skill and regulatory knowledge.
Tailored Defenses for HIPAA, PCI, and FINRA
Healthcare providers must enforce HIPAA and HITECH standards, which explicitly mandate the encryption of ePHI in transit and at rest, regular audit logs, and incident reporting. Law and finance firms face PCI-DSS or FINRA requirements with similar controls.
Blueclone Networks, for example, builds tailored email security strategies combining compliance assessment, advanced threat hunting, incident response preparation, and routine testing. This approach delivers more than just security; it ensures adherence to industry mandates and proactive defense.
Integration with Co-Managed IT and Internal Teams
In-house IT teams often benefit from co-managed models, leveraging outside expertise for the design, testing, and maintenance of sophisticated email security solutions while maintaining local control and user support. This collaboration is particularly valuable during transitions, cloud migrations, or after a security incident.
Proven Track Record and Auditable Results
Professional email protection services provide documentation of incidents blocked, suspicious activity, configuration changes, and user training results. This is invaluable during compliance audits or if regulators probe after an incident.
According to a recent ISACA State of Cybersecurity 2026 report, mid-sized firms with managed or co-managed IT support experienced nearly 45% fewer critical data breaches compared to those relying solely on in-house expertise (source).
Continuous Defense, Not Just One-Time Fixes
Threat actors never stand still. Professional vendors monitor security intelligence feeds, keep defenses up-to-date, and react in real time to emerging threats. This minimizes gaps that can be exploited when your team is focused elsewhere.
Economies of Scale and Expertise
Utilizing providers deeply familiar with NJ’s regulatory and business climate ensures faster incident response and less disruption. Vendors like Blueclone Networks serve businesses in Princeton, Trenton, Newtown, Philadelphia, and the NYC metro with a localized, compliance-first approach, maximizing business continuity.
For businesses handling sensitive client or patient information, the cost of investing in advanced email security is marginal compared to the loss of reputation, regulatory fines, or downtime recovery costs.
Choosing Between Cloud-Based and On-Premise Email Security Gateways
Selecting the right email security gateway can be a daunting task, especially as organizations move from on-premise servers to cloud-hosted solutions. Each deployment model offers distinct benefits, and presents unique risks.
On-Premise Email Security Gateways
Traditional on-site security appliances still have a role in organizations with strict internal controls or legacy applications. They provide local data jurisdiction and may offer performance advantages for businesses with centralized offices. However, maintenance, patching, and hardware refreshes become an ongoing responsibility for internal teams.
Organizations anchored to on-premise models must remain vigilant, as attackers often target outdated software or misconfigurations in these environments. Regular audits, vulnerability assessments, and timely updates are mandatory to keep advanced threats at bay.
Cloud-Based Email Security Gateways
The rise of secure mail hosting in the cloud, whether with Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, or another platform, shifted much of the security burden to service providers. Cloud-based gateways offer several advantages:
- Scalability: Easily adjust capacity as your workforce expands or contracts
- Centralized Management: Streamlined policy enforcement across multiple offices or remote teams
- Real-Time Updates: Access the latest threat intelligence and automated patches without waiting on internal IT
- Resilience: Redundant, geo-distributed infrastructure minimizes downtime
However, trusting the cloud doesn’t make your business immune. Misconfigured access controls, improperly set sharing permissions, or outdated authentication can still put data at risk. Relying on default security settings may leave critical gaps unaddressed.
A hybrid model, utilizing both cloud and local gateways, can provide extra layers of email security. This is particularly helpful for healthcare, legal, and finance companies needing to enforce jurisdictional data residency or comply with industry-specific encryption requirements.
Strategic Consideration: When choosing an email security gateway, prioritize solutions with support for multi-factor authentication, robust logging, policy-based encryption, and seamless integration with your existing IT stack. Evaluate vendors not just on features, but on their ability to align with your compliance, risk tolerance, and growth trajectory.
Email Security Best Practices for SMBs in Healthcare, Legal, and Finance
Small and mid-sized organizations in regulated sectors remain top targets for email-based threats. However, limited resources often force SMBs in Princeton, Trenton, and beyond to make hard decisions about which security controls to implement first. Here’s a pragmatic blueprint:
1. Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for All Accounts
Mandatory MFA prevents over 99% of credential-based attacks, significantly raising the bar for cybercriminals.
2. Harden Access Controls and Deactivate Unused Accounts
Regularly audit user accounts on your mail server. Disable access for former employees promptly. Use least-privilege access wherever possible.
3. Leverage Advanced Email Security Gateways
Invest in gateways with real-time scanning, URL rewriting, anti-malware sandboxing, and protections against spear-phishing and BEC. Confirm these defenses are active for both inbound and outbound messages.
4. Encrypt Sensitive Communications
Apply end-to-end encryption for emails containing PHI, client financials, or other regulated data. Educate your staff on how and when to use encryption features.
5. Regular User Training and Simulated Phishing
Conduct staff training at least quarterly. Use simulated phishing tests to help users recognize malicious emails without real-world consequences.
6. Strong Outbound Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Prevent accidental or intentional leaks by setting DLP rules for sensitive keywords, attachments, and regulated client or patient identifiers.
7. Maintain Continuous Backup and Recovery Solutions
A comprehensive email security plan includes regular, automated backups to offsite or cloud platforms. Test your recovery process regularly.
8. Centralized Logging and Incident Response
Aggregate logs from all email protection services and gateways. Have a clear, documented incident response plan ready before you need it.
Connect with Blueclone Networks now to get a tailored best-practice guide, customized for your compliance needs and business size.
Real-World Example
A New Jersey-based healthcare network recently deployed advanced email security after suffering two BEC attacks in six months. By implementing MFA, layered filtering, routine staff training, and real-time monitoring, they not only achieved full HIPAA compliance but saw a 90% drop in phishing-related incidents within the first year. Their experience mirrors data from the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency, which notes that multi-layered email defenses reduce incident response costs by over a third (source).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Email Server Security
Common signs include users reporting unexpected password changes, emails sent from your domain without authorization, sudden spikes in spam or phishing messages, and login attempts from unfamiliar locations. IT teams should also watch for failed logins, unrecognized configuration changes, or third parties contacting you about suspicious messages originating from your domain.
While basic spam filters block bulk unwanted mail, an email security gateway inspects attachments, URLs, and message content for malware, phishing attempts, spoofing, and business email compromise. Advanced gateways apply multiple layers of scanning, integrate with authentication protocols, and offer real-time updates against emerging threats.
Encryption ensures that if messages are intercepted, either in transit or at rest, they remain unreadable to unauthorized parties. Secure mail hosting may protect your infrastructure, but only encryption defends each message’s content, which is essential for compliance in regulated industries.
BEC is a type of cyberattack in which criminals use social engineering to trick employees into transferring money or sensitive information by impersonating executives, partners, or trusted vendors. Its prevalence stems from the human factor: even well-protected technical systems may fall prey to convincing, personalized messages that exploit trust.
Many organizations benefit from external expertise, especially as attackers grow more advanced. Outsourcing does not replace internal IT; rather, it supplements existing skills with up-to-date defense strategies, access to the latest threat intelligence, and dedicated resources for monitoring and incident response. For businesses facing compliance or resourcing challenges, this partnership can be invaluable.