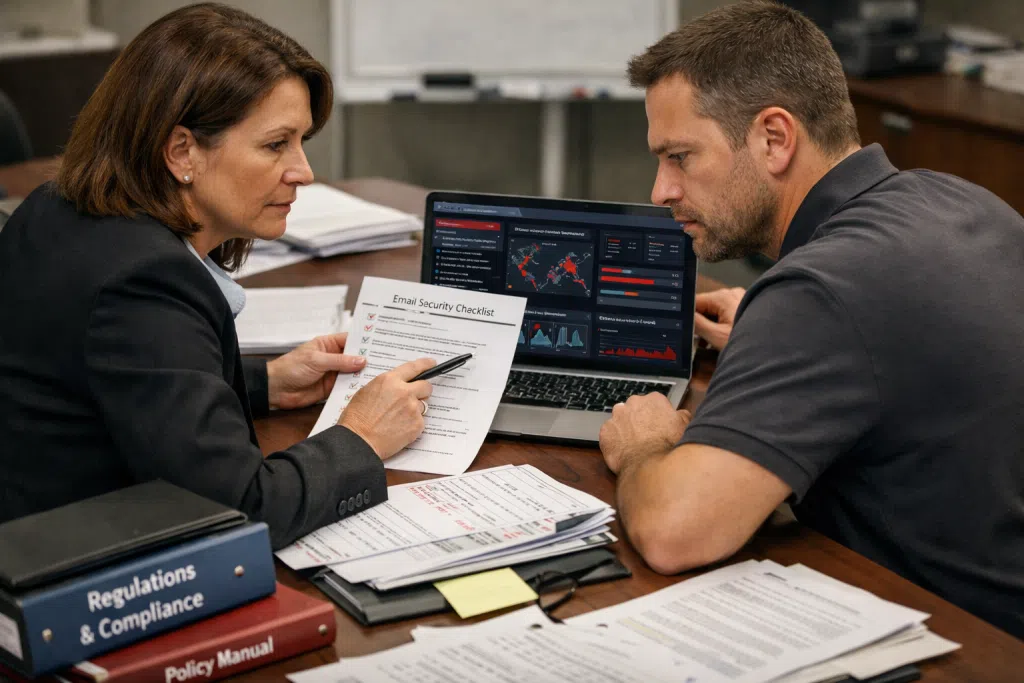
Understanding Email Security Checklists and Their Role in Compliance
Email remains the backbone of business communication, but it’s also among the most common routes for cyberattacks and compliance breaches. For organizations across regulated industries, healthcare, legal, finance, and more, maintaining email security is not simply about protecting information; it’s about staying on the right side of the law. An email security check serves as a practical guide, ensuring all aspects of digital correspondence follow security and privacy guidelines. But why does this matter beyond obvious threats like phishing? And can a checklist really help organizations maintain complex regulatory compliance?
At the heart of many data regulations is the need to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, leaks, or manipulation. Email systems can be exploited in multiple ways: phishing attempts deliver malware, man-in-the-middle attacks intercept communications, or social engineering tricks staff into sending confidential client files to threat actors. Healthcare providers, for instance, must constantly demonstrate their use of HIPAA-compliant email solutions. Law firms and financial advisors are required to ensure business email security withstands attempts at wire fraud and data breaches.
An effective email security checklist doesn’t just flag these risks. It frames actionable steps for admins and end users, covering technical setups, user protocols, and ongoing monitoring. For SMBs in regulated sectors across New Jersey, Eastern Pennsylvania, and New York City, these checklists have evolved from “nice to have” to operational essentials.
Essential elements commonly included in a robust email security check are multi-factor authentication, email encryption, user training, ongoing monitoring for threats, and regular security audit cycles. Aligning checklist items with standards such as HIPAA, FINRA, and PCI-DSS not only helps prevent breaches, but it also provides a paper trail proving diligence for regulatory audits.
Still, even the best checklist is only as good as its adoption and enforcement. It must be updated as regulations change and cyber threats evolve. Tools like secure email hosting and system-level protections are crucial layers that reinforce these checklist-driven habits.
For business leaders striving to secure company data and build a defensible compliance posture, the stakes are too high for guesswork. That’s why a systematic email security check brings structure, visibility, and consistency to policies and day-to-day operations. Want to understand how your approach stacks up? Connect with Blueclone Networks now.
Building a Smart Email Security Checklist: What Should It Cover?
A credible email security checklist should reflect your industry’s regulatory environment, company size, technology stack, and the sensitivity of data handled. In the context of businesses across Central New Jersey and the NYC metro area, where regulations frequently govern every email, there are a few non-negotiable areas every checklist must address.
- User Access Controls: Start with the basics: are accounts protected by strong, unique passwords and multi-factor authentication? It’s vital to restrict admin privileges to only those who need them. Ensure each email account is tied to an active employee; stale or shared accounts are prime targets for breaches.
- Email Encryption: Protecting messages both in transit and at rest is a must, especially for HIPAA compliant email. Use encryption protocols like TLS to secure content before it ever leaves your mail server, and insist on encrypted archives for all backup copies.
- Anti-Phishing and Threat Detection: Integrate real-time filtering tools that analyze incoming messages for potential phishing, malware, or business email compromise (BEC) attempts. Modern business email security solutions flag suspicious links, sender spoofing, and other indicators before users even read a message.
- Employee Training and Simulations: Human error remains the number one source of email-based incidents. Make ongoing security training part of your official checklist. Run simulated phishing attacks. Regularly remind staff about reporting suspicious messages and refraining from sharing credentials.
- Incident Response and Reporting: If an attack slips through, what’s the immediate plan? Your checklist should lay out steps for isolating affected accounts, containing threats, investigating the event, and reporting incidents to compliance authorities where applicable.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Audit Logging: Your email security check should ensure mail logs are indexed, retained, and reviewed regularly. Set up alerts for unusual patterns, such as large volumes of outbound mail or multiple failed authentication attempts.
- Third-Party App Controls and Integrations: Review and approve third-party plugins or applications linked to company email. Disable unnecessary integrations, regularly audit permissions, and watch for apps that could leak sensitive data.
- Backup and Recovery: Ensure email data is backed up to secure, access-controlled environments with regular restore tests. For regulated firms, this might include off-site encrypted storage and disaster recovery planning.
- Regular Updates to Security Protocols: The threat landscape and compliance rules change constantly. Update your checklist on a quarterly basis, or whenever major regulations like HIPAA or PCI-DSS are revised.
Let’s consider a practical example. A specialty medical practice in Princeton, NJ, must not only deploy encrypted mail solutions; it must also log access to protected health information, regularly run employee phishing drills, and show regulators evidence of incident response plans. Similarly, a law firm is mandated to preserve client-attorney privilege by controlling outbound mailbox permissions and retaining comprehensive audit logs.
Missteps here aren’t just technical liabilities; they expose your company to legal penalties and reputational damage. Keeping the checklist relevant and actionable is what separates organizations that sail through compliance reviews from those scrambling to plug holes after an incident. For mid-sized businesses ready to audit or overhaul their approach, download or review the most recent guidelines provided by Blueclone Networks for effective business email security and email protection.
The Link Between Compliance Frameworks and Email Security Best Practices
For entities bound by regulations such as HIPAA, HITECH, PCI-DSS, FINRA, or the New Jersey State privacy laws, compliance is an ongoing obligation, not a one-time fix. Email systems are specifically cited in nearly every data privacy and security framework because they are a prime attack vector for extracting sensitive information.
A modern email security check aligns closely with the mandates and controls found in these compliance frameworks:
- HIPAA requires the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all protected health information (PHI), which includes electronic transmissions via email. If a healthcare organization fails to encrypt PHI or does not document incident response steps, steep fines may follow.
- PCI-DSS governs payment card data, demanding that cardholder information never be sent in plaintext emails and that access is limited to authorized personnel.
- FINRA and SEC enforce rules on communication retention and monitoring for financial services. Emails containing client investment decisions or trade information must be archived securely, and any unauthorized access must be reported quickly.
According to a February 2026 report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 82% of small and midsized businesses that suffered an email breach had overlooked at least one checklist item related to MFA or email encryption, underscoring the importance of following detailed procedures.
More than a legal safeguard, a checklist-driven approach serves as both a preventive and detective strategy. It instills repeatable behaviors, like consistent archival, regular audits, and periodic incident response drills, that help demonstrate compliance during external reviews.
Many email security best practices originated from compliance-driven requirements: enforcing strong passwords, mandating encryption, alerting on suspicious logins, and keeping retrievable records of all significant user activity. Some advanced firms in high-compliance environments now integrate their email security check directly into regular IT risk assessments and compliance reports for executive oversight.
Failure to adopt these practices and to document them is a leading factor in compliance violations and regulatory findings. For this reason, businesses handling sensitive data, especially those required to implement secure email hosting, often include independent audits or turn to reputable MSPs for routine assessments.
Thinking about your next audit cycle? These practices are already being delivered by experienced providers, including Blueclone Networks, built to serve regulated SMBs with advanced email protection. To make sure you’re not missing a vital step in your compliance journey, review a sample compliance-aligned checklist and don’t hesitate to reach out for a tailored assessment.
Email Security Checklists in Action: Lessons from the Regulated Sector
Theory matters, but email security lives or dies in daily execution. Regulated businesses in and around Princeton, NJ, including healthcare clinics, legal practices, and financial advisories, have navigated the realities of implementing, updating, and enforcing robust email security checklists.
Consider a medical billing group recently audited by federal regulators: their routine email security check included regular, documented phishing drills, detailed logs for suspicious login attempts, and mandatory MFA across all user accounts. When presented to compliance auditors, these records demonstrated a proactive stance and a clear chain of accountability, resulting in a quick resolution and zero fines.
In another instance, a boutique law firm in Trenton avoided a costly wire fraud attempt because their weekly email protection workflow required manual verification for all requests involving banking details. Their system also flagged and quarantined suspicious attachments in real time, actions that only happened because those checks were written, monitored, and enforced as part of a living checklist.
SMBs often struggle to balance day-to-day business with rigorous security. Yet, according to a March 2026 research update from the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), 62% of small organizations that experienced breaches in the last 12 months had experienced gaps in checklist enforcement or skipped essential training refreshers. These lapses frequently stemmed from the “set it and forget it” mindset, mapping risks once, then letting policies grow stale while attackers evolve.
On the opposite side, those who drive a “living checklist” culture, updating protocols quarterly, training on emerging phishing lures, and integrating automation to spot threats, see far fewer major incidents. Automated testing, third-party audits, and dynamic alerts all spring from this checklist mindset.
While manual checklists remain valuable, the most sustainable results are achieved when these processes intersect with technology controls and expert oversight, both human and automated. For growing firms, this means integrating checklist compliance with tools like secure email hosting, advanced threat monitoring, and expert-led training sessions.
Need help putting these lessons into practice? Connect with Blueclone Networks now for compliance-driven email security audits and custom action plans.
Optimizing Your Business Email Security: Tools, Solutions, and Continuous Updates
The world of email security is never static. Threat actors introduce new tactics continuously, and regulations adapt in response. For organizations aiming to keep email security checklists relevant and effective, adopting a blend of human processes and technology safeguards is critical.
Cloud-based Filters and AI-Powered Threat Detection: Modern secure email hosting platforms deliver native anti-phishing, malware sandboxing, and outbound link scanning. These systems analyze message patterns and flag potentially harmful emails before they reach inboxes. For SMBs in regulated sectors, this technology layers seamlessly over traditional checklist-driven processes.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies: DLP monitors outbound email traffic for signs of sensitive information, credit card numbers, protected health data, or legal records, leaving the organization. With the right configurations, these systems automatically block or quarantine non-compliant outbound messages.
Automated Archiving and Retention: Effective business email security includes automated compliance archiving, with retention policies mapped to HIPAA, FINRA, or PCI-DSS requirements. This ensures audit trails remain intact and discoverable, saving staff countless hours in the event of an investigation or lawsuit.
User Activity Monitoring and Behavioral Analytics: By tracking how users interact with email, such as access times, device locations, or abnormal sending patterns, security teams receive early warnings of compromised accounts or insider threats. This approach extends checklist items into automated real-time mitigation.
Integrated Incident Response Platforms: Fast, coordinated response matters when an incident occurs. Platforms that tie together email security, logging, and ticketing workflows help organizations execute their incident response checklist rapidly, reducing potential damage and regulatory fallout.
Regular Security Awareness Training: While not strictly a software solution, quarterly staff training, backed with up-to-date content from industry partners or reputable institutions, ensures employees remain the first line of defense, aware of emerging scam tactics and social engineering risks.
According to a 2026 whitepaper by Gartner, companies using integrated platforms for email protection paired with checklist-driven policies experienced up to 40% fewer breaches and substantially faster compliance audit resolutions.
For businesses in regulated environments, partnering with firms equipped for ongoing compliance support can be a game-changer. Blueclone Networks, for example, not only offers state-of-the-art tools for HIPAA-compliant email but also works with companies to revise and optimize their checklists as threats and compliance standards shift. This alignment drives both cost-effective operations and a stronger security posture.
Is your current approach leveraging proven cloud tools and continuous improvement agendas? Don’t let checklists gather dust – combine them with the right technology stack for ongoing results.
Common Pitfalls and How to Strengthen Your Email Security
Even the most comprehensive email security checklist can fall short without ongoing vigilance and buy-in across all levels of an organization. Businesses in regulated fields often make a handful of recurring mistakes that compromise their overall compliance strategy.
Neglecting User Training: Overlooking routine training leaves users vulnerable to phishing campaigns, credential harvesting, or social engineering ploys. A well-crafted email security check always features regular, tracked employee education with follow-up simulations.
Stale Policies and Outdated Procedures: Security protocols written during an annual audit and forgotten for months create major gaps. Schedule quarterly reviews, update your checklist as new threats are discovered, and keep policies public to ensure they are adopted widely throughout the organization.
Ignoring Shadow IT and Unauthorized Applications: Employees sometimes link unapproved cloud apps or messaging services to their email platforms, undermining secure email hosting. The checklist should require regular reviews of integrated apps and revoke unnecessary permissions.
Poor Incident Documentation: After a suspected breach, regulatory frameworks demand prompt and accurate documentation. Failing to log incident findings, escalation steps, and remediation actions unveils significant risk in future compliance audits.
Lack of Third-Party Assessment: Self-evaluations rarely catch everything. Bringing in independent auditors or leveraging managed security partners delivers an outside perspective, often catching vulnerabilities missed internally.
Adopting a thorough and adaptive email security check is about progress, not perfection. Building strong feedback loops, consistently applying the checklist, and cultivating a culture where staff actively report risks are practical steps every regulated business should follow.
If these pitfalls sound familiar, or if your team is unclear on their current protocols, consider a compliance health check now. Connect with Blueclone Networks for a deep dive into proven strategies to elevate your business email security, secure sensitive communications, and streamline compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Email Security Compliance
For regulated companies, the core element is verifying that both technological safeguards (like encryption and anti-phishing filters) and human processes (such as user training and incident response) are in place and up to date. No single item is enough on its own; it’s the combined effect that holds up in compliance audits.
Best practice recommends quarterly updates or whenever regulations change. Cyber threats and compliance rules evolve rapidly, so what kept you secure last year may not cover today’s risks.
Yes, HIPAA also demands strict access controls, comprehensive logging, periodic risk assessments, staff training, and documented incident response, encryption alone is not enough. Each element should be addressed within your email security check and reinforced with technology solutions.
Non-compliance can lead to regulatory fines, legal disputes, reputational harm, and lost business. Regulatory bodies often review adherence to written policies, so maintaining an up-to-date and actionable checklist is crucial for defense during audits or investigations.
Many SMBs work with managed security providers who supply ready-made checklists, deliver user training, run audits, and help enforce ongoing technical safeguards. Outsourcing this expertise is often more practical and cost-effective than hiring dedicated security personnel.